Analog Stethoscopes
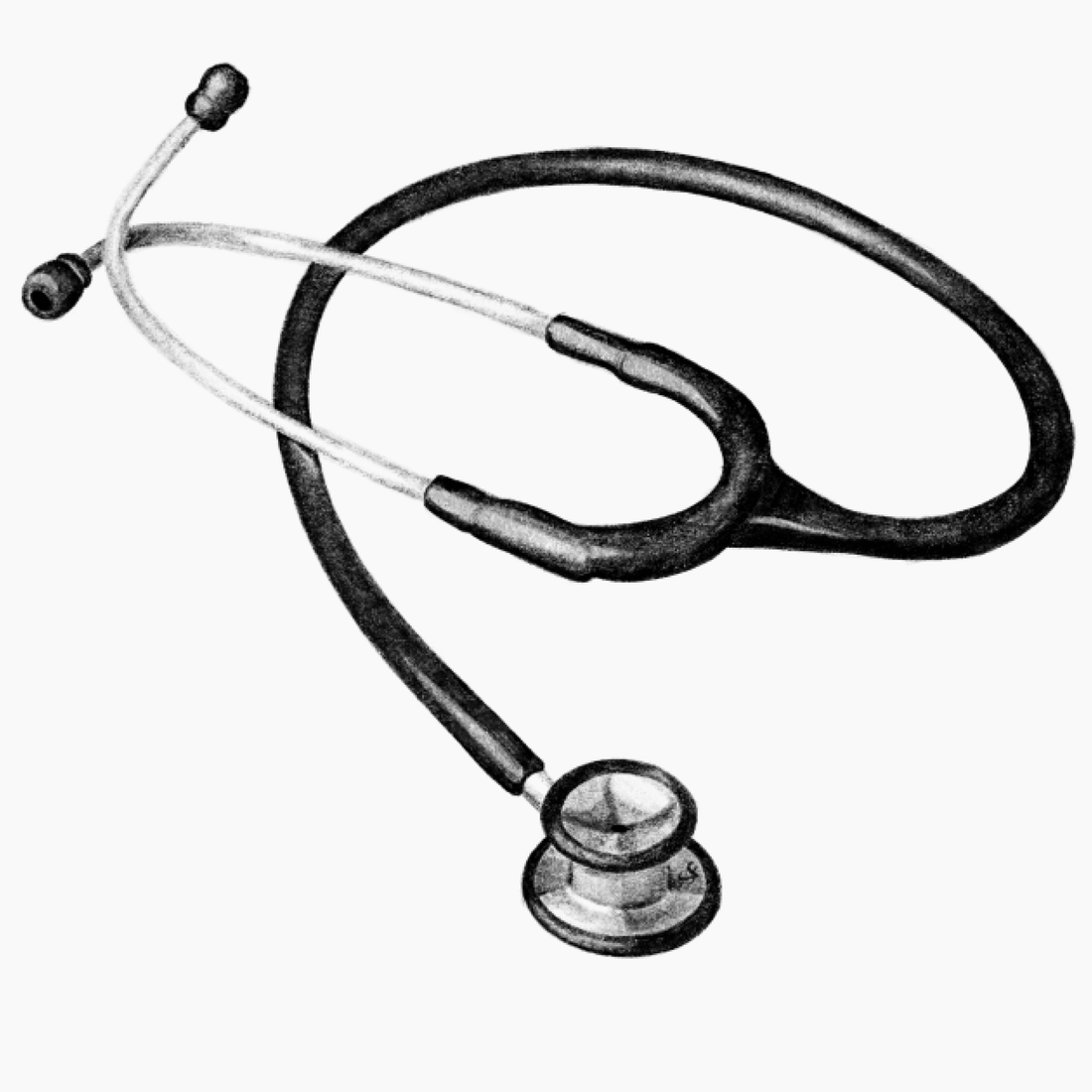
Overview
The stethoscope is a medical device used for auscultating the internal sounds of the body. When placed on the body, vibrations are transmitted through the chestpiece, creating acoustic pressure waves that travel through the tubing to the ear tips of the stethoscope. The human ear then translates these pressure waves into sound, allowing clinicians to hear and analyze sounds in relation to the patient's condition.
Headset
The stethoscope headset consists of two ear tubes and ear tips. The ear tips are typically removable and can be easily exchanged to achieve a better fit. For the best sound quality, insert the earpieces into the ear canal such that they are pointing forward — away from the body and toward the bridge of the nose.
 Headset usage diagram depicting proper way to insert ear tips.
Headset usage diagram depicting proper way to insert ear tips.
Chestpiece
The head of the stethoscope is placed on the patient's skin and is responsible for conducting sound. A standard chestpiece has two sides, the diaphragm and bell, which can be switched between by rotating the chestpiece 180 degrees. When the diaphragm is activated, the bell will be deactivated to prevent sound from coming through, and vice versa. Tap on the chestpiece to check which side is activated.

Bell
The bell is the smaller circular side of the chestpiece. It's used to pick up lower frequency sounds and is designed to be used on pediatric patients.
Diaphragm
The larger circular side of the chestpiece is called the diaphragm. The diaphragm is used to pick up sounds with higher frequencies.

Medical Advice Disclaimer
DISCLAIMER: THE CONTENT SET FORTH HEREIN DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE OR IS AN ATTEMPT TO PRACTICE MEDICINE
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images, and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. No material on this website or document are intended to be a substitute for professional medical education, advice, diagnosis, or treatment.